

Of the estimated 4 million babies born in the US each year, up to 35% of them may have difficulties with reflux in the first few months of their lives, known as 'spitting up'. Children may have one symptom or many no single symptom is universal in all children with GERD. Inconsolable crying, refusing food, crying for food and then pulling off the bottle or breast only to cry for it again, failure to gain adequate weight, bad breath, and burping are also common.

GERD in children may cause repeated vomiting, effortless spitting up, coughing, and other respiratory problems, such as wheezing. Symptoms may vary from typical adult symptoms.
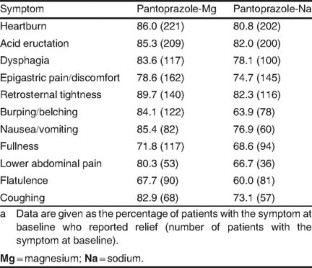
GERD may be difficult to detect in infants and children since they cannot describe what they are feeling and indicators must be observed. Other complications can include aspiration pneumonia.

GERD sometimes causes injury of the larynx (LPR). Esophageal adenocarcinoma – a form of cancer.Barrett's esophagus – intestinal metaplasia (changes of the epithelial cells from squamous to intestinal columnar epithelium) of the distal esophagus.Esophageal strictures – the persistent narrowing of the esophagus caused by reflux-induced inflammation.Reflux esophagitis – inflammation of esophageal epithelium which can cause ulcers near the junction of the stomach and esophagus.These injuries may include one or more of the following: GERD sometimes causes injury to the esophagus. The acid reflux can induce asthma attack symptoms like shortness of breath, cough, and wheezing in those with underlying asthma. Less common symptoms include pain with swallowing/ sore throat, increased salivation (also known as water brash), nausea, chest pain, coughing, and globus sensation. The most common symptoms of GERD in adults are an acidic taste in the mouth, regurgitation, and heartburn. In 1934 gastroenterologist Asher Winkelstein described reflux and attributed the symptoms to stomach acid. The classic symptoms of GERD were first described in 1925, when Friedenwald and Feldman commented on heartburn and its possible relationship to a hiatal hernia. Occasional gastroesophageal reflux without troublesome symptoms or complications is even more common. In the Western world, between 10 and 20% of the population is affected by GERD. Medications include antacids, H 2 receptor blockers, proton pump inhibitors, and prokinetics. Lifestyle changes include not lying down for three hours after eating, lying down on the left side, raising the pillow/bedhead height, losing weight, avoiding foods which result in symptoms, and stopping smoking. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery for those who do not improve with the first two measures. Diagnosis among those who do not improve with simpler measures may involve gastroscopy, upper GI series, esophageal pH monitoring, or esophageal manometry. Acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, which is at the junction between the stomach and the esophagus. Medications that may cause or worsen the disease include benzodiazepines, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, NSAIDs, and certain asthma medicines. Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and taking certain medicines. Complications include esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus. Symptoms include the taste of acid in the back of the mouth, heartburn, bad breath, chest pain, regurgitation, breathing problems, and wearing away of the teeth. Gastroesophageal reflux disease ( GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease ( GORD) is a chronic condition in which stomach contents and acid rise up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
